What Is a Healthcare Supply Chain?
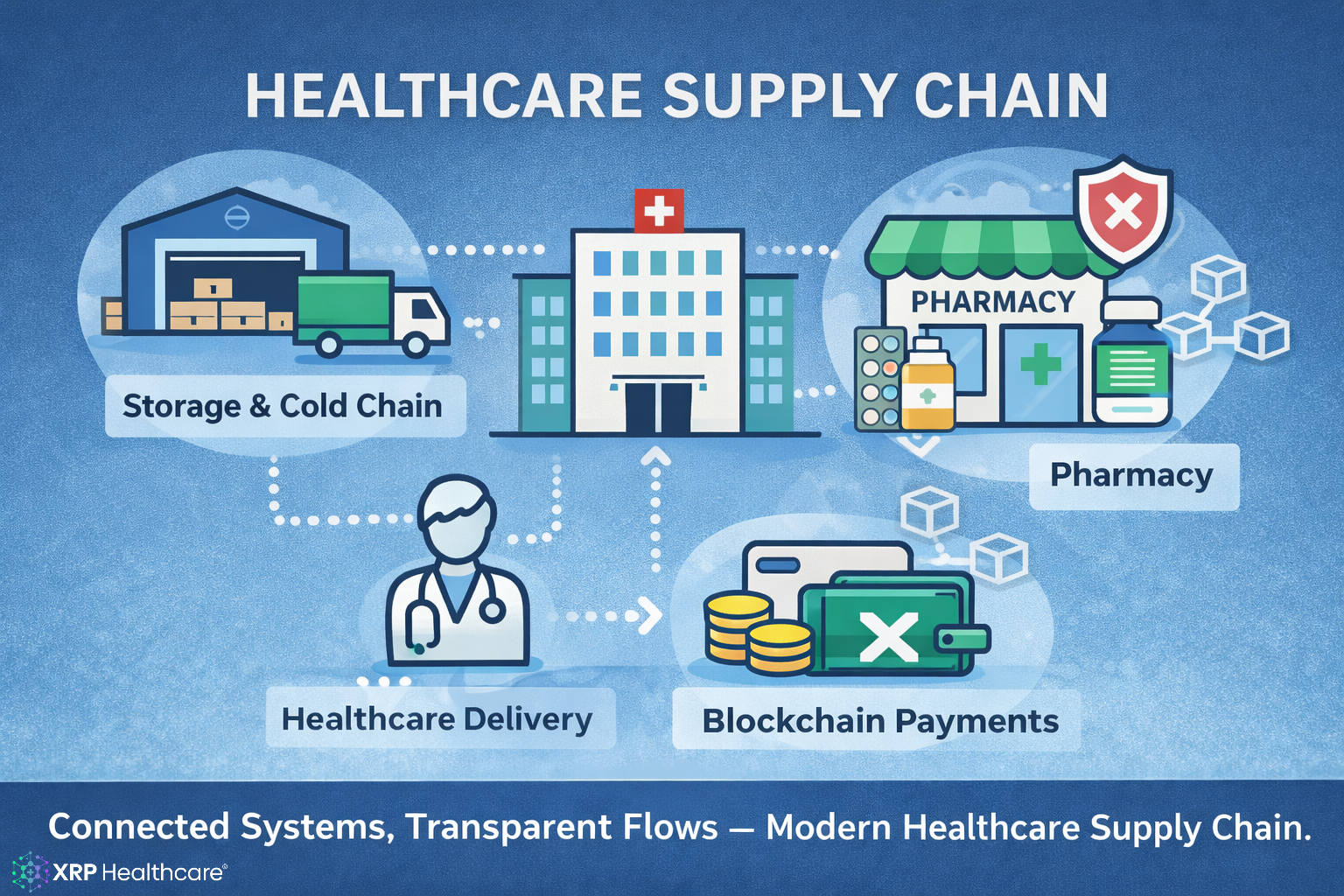
A healthcare supply chain is the network of people, systems, and processes that deliver medical products and services. It starts with manufacturers and ends with patients through clinics, hospitals, pharmacies, and caregivers. Key steps include procurement, storage, transport, inventory management, and delivery. Efficient supply chains ensure medicines and equipment reach the right place at the right time without waste or delay.
(Source: CDC Public Health Supply Chain)
Modern healthcare delivery relies on smooth flow and coordination throughout the supply chain.
Why the Healthcare Supply Chain Matters
Ensures Patient Safety and Care
A strong supply chain prevents shortages of vital medicines and devices. It reduces the risks of errors in delivery or storage. Safe handling of sensitive medicines (cold-chain products) is critical for efficacy. (Source: World Health Organization)
Reduces Cost and Waste
Inefficient supply chains increase cost through expired stock or emergency orders. Digitizing logistics and forecasting demand can cut waste and lower spending. Hospitals and pharmacies can free up capital for other patient services.
Supports Rapid Response in Emergencies
In pandemics or disasters, a well-organized supply chain is vital. Quick distribution of vaccines, treatments, and protective gear saves lives. Tracking systems help ensure availability in all regions.
How Technology Enhances the Healthcare Supply Chain
Digital Tracking and Traceability
Healthcare supply chains benefit from real-time tracking of products from origin to delivery.
RFID tags, barcodes, and IoT sensors help monitor conditions like temperature, humidity, and location. This reduces loss and helps maintain quality.
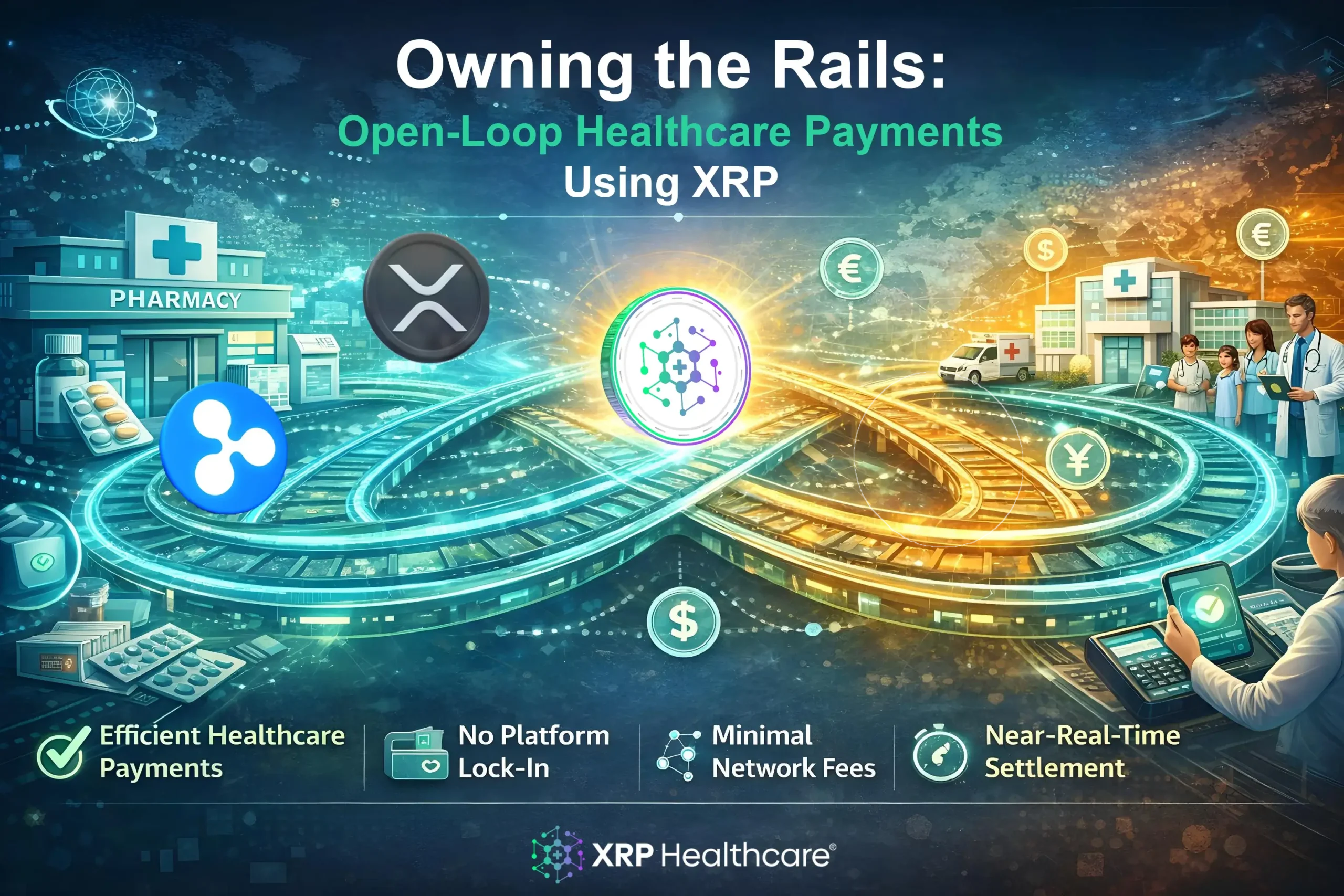
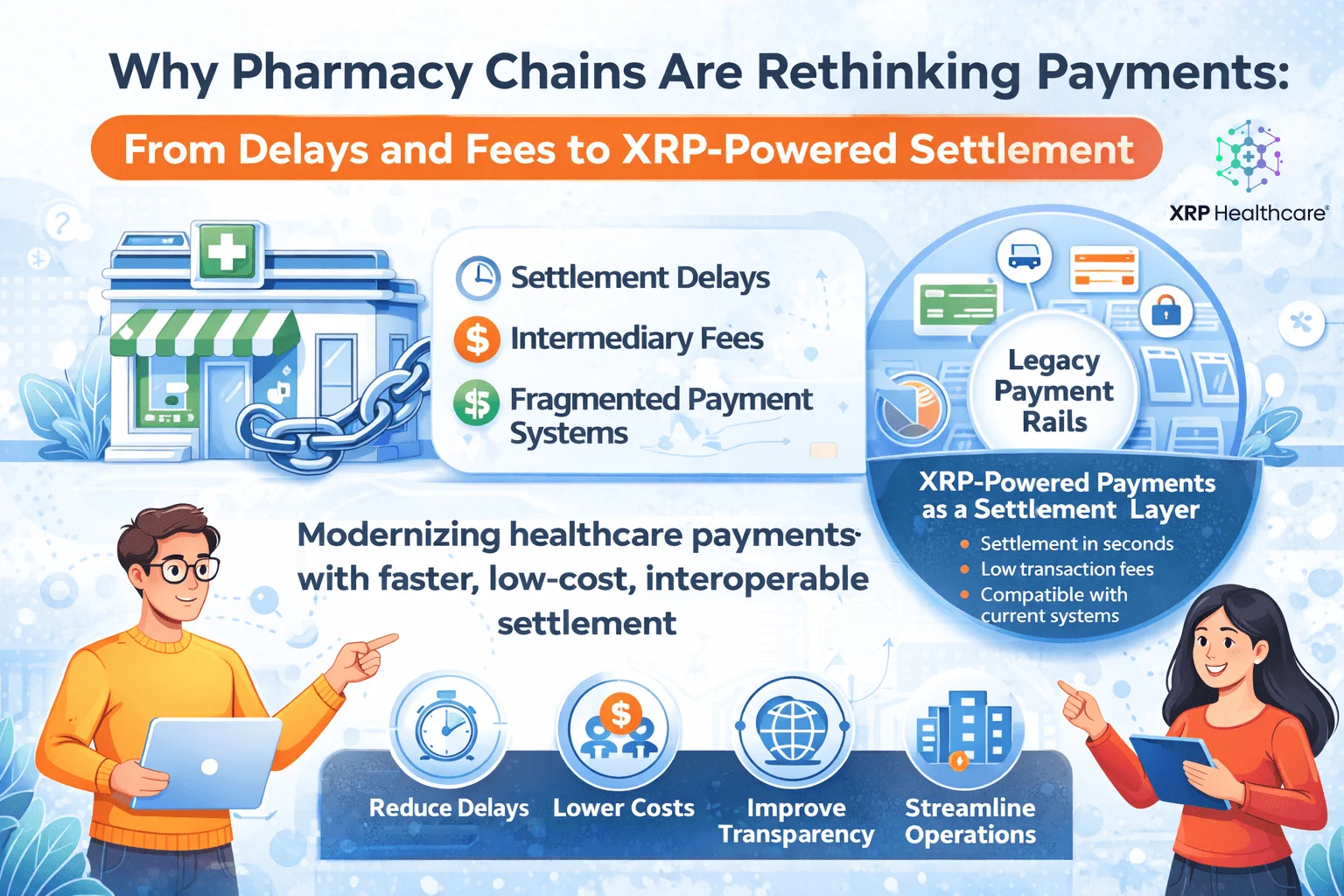
Blockchain for Visibility and Payments
Blockchain systems, like tools built on the XRP Ledger, add transparency and immutability to supply chains. They record transactions securely so that every step is traceable. For example, XRPH Wallet integrates fast, secure payments into healthcare workflows. This supports near-real-time settlement and lowers transaction costs across the network.
(Source: XRP Healthcare XRPH Wallet Info)
Blockchain can help with vendor reconciliation and compliance reporting.
Real-World Supply Chain Examples
Hospitals and Clinics
Hospitals need steady supplies of medicines, devices, and consumables. Advanced inventory systems predict usage and trigger automated orders before stock runs out. This improves patient care and lowers emergency spending.
Global Vaccine Distribution
Global vaccination programs require precise logistics planning. Supply chains must handle cold storage, customs, and coordinated delivery schedules. Advanced systems track every step until doses reach clinics.
Challenges in Healthcare Supply Chains
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare supply chains must follow strict laws for safety, labeling, and tracking. Different countries have varying rules for pharmaceutical imports and exports.
Fragmented Systems
Many supply chains suffer from isolated systems that do not share data. This creates bottlenecks and leads to miscommunication or delays.
Security and Fraud Risks
Counterfeit medicines are a major global concern. Robust tracking and secure records help protect against fake products entering the system.
Future of the Healthcare Supply Chain
- Automation: Robotics in distribution centers speeds processing.
- AI & Forecasting: Predictive models improve stock planning.
- Blockchain: Trusted record-keeping and faster financial settlement.
- Real-Time Data: Better decisions with live status updates.
Conclusion
The healthcare supply chain connects manufacturers, logistics partners, hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. It ensures safe, efficient, and cost-effective delivery of medicines and medical products. Emerging technologies, such as digital tracking and blockchain payments, make supply chains more transparent and reliable. This benefits patients, providers, and healthcare systems worldwide.